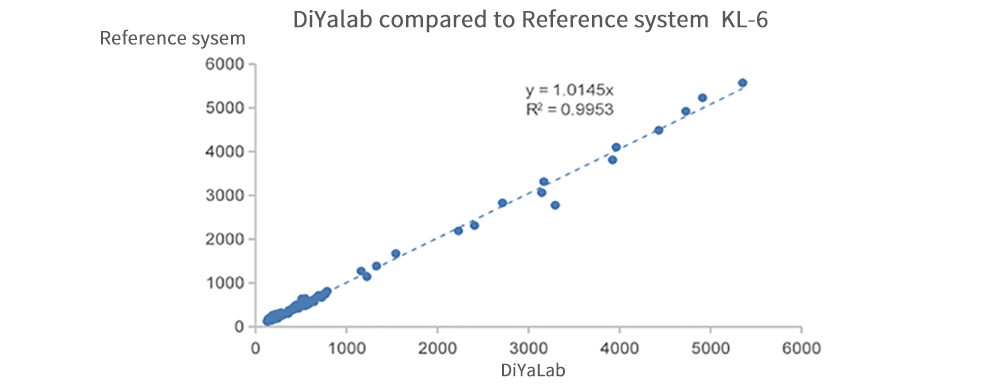
Salivary Glycogen-6 (KL-6) is a sensitive, specific, early and noninvasive marker for the diagnosis of interstitial pneumonia
KL-6 was first identified in Japan. In the presence of interstitial lung disease (ILD), the alveolar epithelial cells of the patient proliferated significantly, resulting in increased expression of KL-6 on the alveolar surface. At the same time, damage to the basement membrane of the alveolar leads to increased vascular permeability, so KL-6 can be tested in the blood.
A large number of studies have shown that serum KL-6 has high specificity and sensitivity for the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD), and continuous monitoring can be used as an important indicator to evaluate ILD activity, severity and prognosis.
|
Assay Name |
Methodology |
Sample type |
|
KL-6 |
Latex enhanced immunoturbidimetry |
Serum |